A RAID log is a project management tool that tracks risks, actions, issues, and decisions.
When it comes to project management, keeping a tight grip on risks and issues is paramount, especially for small and midsize businesses. Enter the RAID log—short for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies—a potent instrument for adeptly navigating these challenges. If you're a business owner eager to broaden your technical know-how, this guide is your key to understanding the ins and outs of a RAID log and mastering its utilization.
What is a RAID log?
A RAID log is a comprehensive document that captures and organizes essential project-related information. It serves as a centralized repository for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies associated with a project, providing a holistic view of potential obstacles and facilitating proactive management.
Consider a software development project for a small business aiming to launch a new eCommerce platform. In this scenario, a potential risk could be the reliance on a specific technology that might face unforeseen compatibility issues or delays in updates. Assumptions might include expecting seamless integration with existing systems while overlooking the possibility of unexpected glitches. Issues could arise from miscommunication among team members, leading to delays in coding and testing phases. Dependencies may surface in the form of external factors, such as relying on a third-party vendor for payment processing, which could introduce delays if their system experiences downtime. These hypothetical examples highlight the diverse nature of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies that a RAID log can help identify and manage in the context of a real-world project.
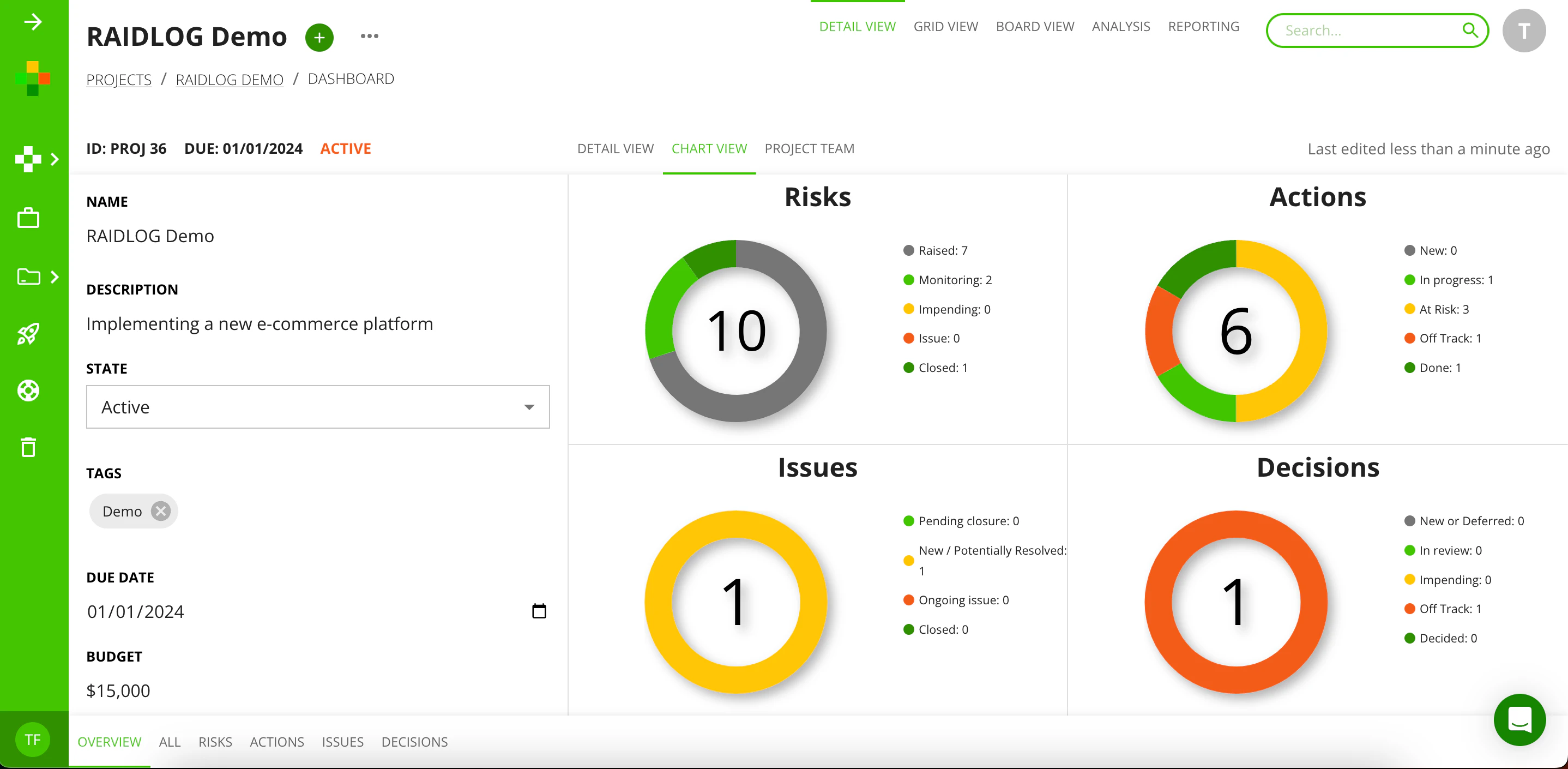
Illustration of a RAID log in Raidlog (Source)
What are the benefits of using a RAID log?
Proactive problem-solving: By identifying risks and issues early, your SMB can proactively address challenges before they escalate, preventing potential project derailments.
Improved decision-making: The RAID log provides a comprehensive project overview, aiding decision-makers in understanding the landscape and making informed choices regarding project direction based on the project's current status.
Stakeholder confidence: Transparency and proactive management instill confidence in external stakeholders when employing your services. They will appreciate your organization’s ability to foresee challenges and mitigation strategies.
Time and resource savings: Addressing issues promptly and having contingency plans in place can save valuable time and resources that might otherwise be wasted on firefighting.
What kind of businesses should consider a RAID log?
Incorporating a RAID log is advantageous for any business, especially small and midsize enterprises engaged in projects of diverse complexities. The benefits of this tool are accentuated when tackling projects marked by tight deadlines, constrained resources, or high stakes.
The implementation of a RAID log becomes particularly essential in such scenarios, providing a structured approach to identifying and managing risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. It serves as a strategic asset for businesses navigating the challenges inherent in projects with heightened time constraints, resource limitations, or significant stakes at play.
Why use a RAID log?
From transparency and easier risk management to the ability to learn from past mistakes, here are some of the most important motivations for using a RAID log:
Visibility and transparency
Projects often involve numerous moving parts and stakeholders, making it challenging to keep everyone informed. A RAID document provides a centralized and transparent view of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies associated with a project. This visibility ensures that all team members and stakeholders are on the same page regarding potential challenges and project status.
Proactive risk management
Unforeseen risks can emerge at any stage of a project, leading to delays and resource overruns. A RAID log allows teams to identify and assess risks early in the project lifecycle. This proactive approach enables the development of mitigation strategies and contingency plans, minimizing the impact of potential issues.
Informed decision-making
When decision-makers lack comprehensive information, they may make suboptimal choices. With a RAID log, decision-makers have a consolidated overview of the project's landscape. This wealth of information empowers them to make informed decisions based on the real-time status of risks, issues, and dependencies.
Continuous improvement
Projects often face recurring challenges, but without a systematic approach, lessons may go unlearned. The RAID log serves as a repository of historical project data. By analyzing past entries and outcomes, teams can identify patterns, learn from experiences, and continuously improve their project management processes.
What are the key features of a RAID log?
A RAID log typically includes sections for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies, with each section detailing specific items. Additionally, it may incorporate priority levels, responsible parties, and action plans for each entry.
When first using a RAID log, it might help to look at some RAID log examples from other departments within your business. You can then use this project RAID log template to come up with your own RAID document.
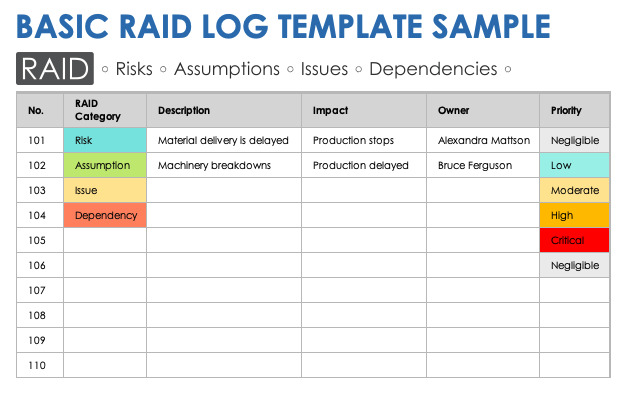
Basic RAID log template sample [1]
How to create and use a RAID log
Implementing a RAID log involves a systematic approach to ensure its effectiveness in managing project risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. Here's a step-by-step guide for SMBs.
Define entry criteria: Clearly outline what constitutes a risk, assumption, issue, or dependency in the context of your project. Establish criteria for entry to maintain consistency.
Identify stakeholders: Determine who will be responsible for updating and managing the RAID log. Assign roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability.
Template design: Develop a project RAID log template that includes necessary fields such as description, impact, probability, responsible party, and action plan. This template will serve as the standardized format for capturing information.
Training and onboarding: Ensure that team members are trained on how to use the RAID log. This includes understanding the importance of each section, the updating frequency, and the escalation process.
Integration with project management tools: Integrate the RAID log with existing project management tools and processes to streamline workflows. This ensures that the RAID log is not a standalone document but an integral part of the overall project management system.
Regular updates and reviews: Establish a schedule for RAID log updates. Regularly review and update entries to reflect the current status of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
Communication plan: Develop a communication plan to inform stakeholders about updates to the RAID log. This ensures that everyone involved is aware of changes and can contribute to discussions as needed.
Analysis and learning: Periodically analyze the RAID log data to identify trends and patterns. Use this information to improve risk management strategies and enhance project outcomes.
RAID log management best practices
Here are a few best practices that can help you get the most benefit from your RAID log.
Prioritize entries: Assign priority levels to each entry in the RAID log. This helps in focusing efforts on addressing the most critical risks and issues first.
Regular risk workshops: Conduct regular huddles/meetings dedicated to discussing and updating the RAID log. This collaborative approach ensures that insights from various team members are considered.
Clear escalation paths: Define clear escalation paths for high-priority risks or issues. Ensure that there is a process in place for escalating matters to higher levels of management if necessary.
Document mitigation strategies: For each identified risk, document mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This proactive approach ensures that teams are prepared to address challenges swiftly.
Periodic audits: Conduct periodic audits of the RAID log to ensure data accuracy and relevance. Remove outdated entries and verify the effectiveness of implemented mitigation strategies.
Customize for project specifics: Tailor the RAID log to suit the specific needs and nuances of each project. A one-size-fits-all approach may not capture the unique aspects of different initiatives.
Encourage open communication: Foster a culture of open communication within the team. Encourage team members to report risks and issues promptly and provide feedback on the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
Take your next steps in project management
Implementing a RAID log is a strategic move for SMBs to fortify project management practices. It's not just a tool; it's a mindset that fosters proactive problem-solving and transparent communication. As you embark on this journey, consider exploring more about project management and related tools with these additional resources:
Note: The screenshots of applications included in this article are examples to show a feature in context and are not intended as endorsements or recommendations.
