Understand your project's progress with the intricacies of a burndown chart.
If you're a project manager overwhelmed by the daily challenges of overseeing tasks, deadlines, and budgets, you're not alone. In fact, 75%* of project managers are in the same boat, juggling multiple responsibilities that demand time and attention. What if there was a tool designed to ease this burden, offering a comprehensive visual aid to track your project's progress and efficiently allocate resources?
Yes, this is the power the burndown chart holds.
Supported by Gartner's research and enriched with valuable insights from Young Pham[1], a seasoned project manager at an online business newswire, this guide unveils the ins and outs of burndown charts.
"In project management, ensuring that every moment is not just counted, but counts, becomes paramount. The burndown chart embodies this principle."


Young Pham
Project Manager at Biz Report
What is a burndown chart?
A burndown chart is a graphical representation used primarily in projects that adopt Agile methodology to illustrate the amount of work remaining in your project versus the time left to complete it. It allows your team to gauge the project's progress and adjust the efforts accordingly easily.
"A burndown chart isn't just your everyday tracking tool; it's a conversation starter. It fosters communication, aligning the team's vision and revealing unseen roadblocks, turning simple lines and dots into a roadmap to success," adds Pham.

What are the crucial components of a burndown chart?
A burndown chart comprises several key components, primarily focusing on the X and Y axes, that demonstrate a project's progress.
X-axis (Time): A horizontal axis that represents the time frame of the project, which can be measured in days, weeks, or sprints. It provides a chronological snapshot of the project's life cycle.
- Y-axis (Tasks): Denotes the work left in the project. It can be measured in hours, story pointsStory points measure a task's complexity and effort, not time, helping teams estimate work more flexibly., or any other unit relevant to the project.
Within these axes lies the essence of the burndown chart's functionality, depicted through two key lines that tell the story of the project's progress:
The burndown line: This descending line represents the actual work remaining in the project. It shows how quickly tasks are being completed relative to the initial projections. A steeper descent indicates rapid progress, while a flatter line or upward tick signals potential issues or slowdowns.
The ideal line: This line showcases the anticipated pace of work completion. Drawn from the starting point to the project's endpoint, it offers a benchmark against which the actual progress (burndown line) can be compared.
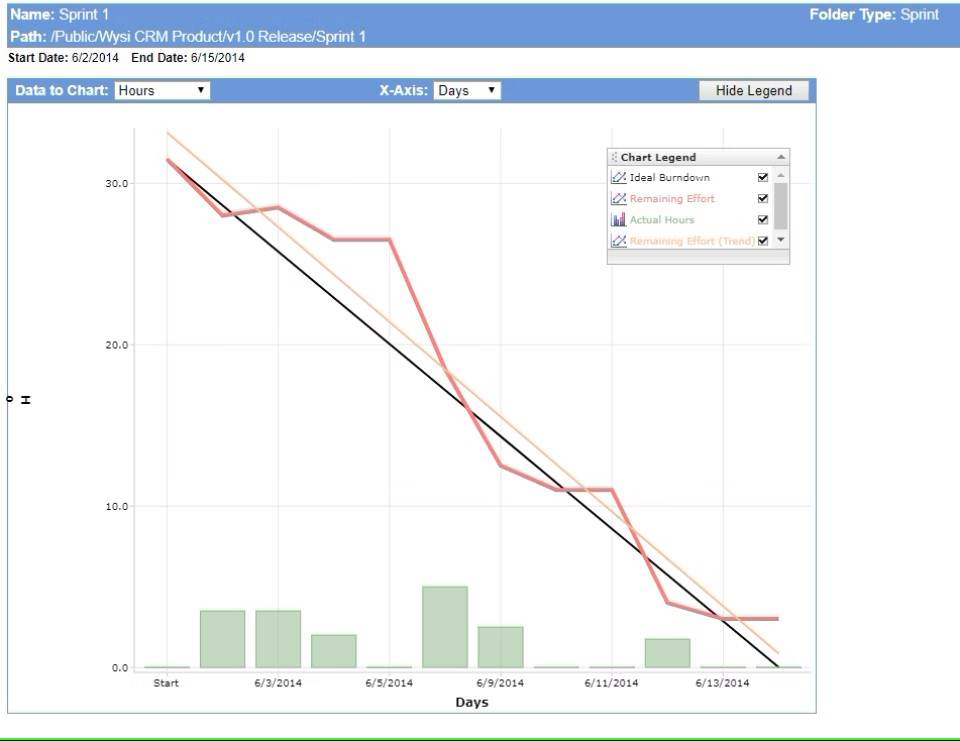
A requirements management tool showcasing burndown and ideal lines (Source)
Why do burndown charts matter?
In Agile project management, the burndown chart distinguishes itself as vital, standing apart from other graphs and charts such as Gantt charts or flow diagrams. Many PMs want the burndown chart functionality in the project management tools they choose because its visual depiction ensures efficient task tracking and completion. For example, if the chart shows an unexpected spike in remaining tasks, quick decisions such as reallocating resources or reprioritizing work can be made on the spot.
Though primarily a visualization tool, burndown charts also act as silent communicators among stakeholders. They offer a common ground for discussion by presenting project status transparently, making it easier for the team to align on objectives and identify areas that need focus.

Pham emphasizes how indispensable a burndown chart can be, especially when facing a tight deadline in software development. He suggests that this tool allows an Agile team to promptly identify daily discrepancies between the ideal work schedule and the actual remaining work. If tasks start piling up, the team can quickly pivot by adjusting resources or reprioritizing tasks. This agility ensures not just meeting deadlines but also maintaining a smooth flow of work throughout the project.
What are the different types of burndown charts?
From tracking the pace of a sprint to guiding the journey of an epic, burndown charts morph into different forms to meet distinct project needs. Here's a clear look at the varied charts and what sets each one apart:
1. The sprint burndown chart: Focuses on the here and now. A sprint burndown chart in the Scrum framework helps a team see how much work is left to complete a single sprint goal. Think of it as a short-term guide, showing what needs to be done day by day.
2. The release burndown chart: A bigger-picture view that tracks progress across multiple sprints. Think of it as a marathon, not a sprint, where the goal is to complete a significant chunk of the project by the release date. It helps the team see how they're doing overall, not just in one small part.
3. The epic burndown chart: This is your long-term lens on project work. It spans multiple releases and aims to track progress on large, overarching goals that often require a considerable amount of time to complete. Unlike the release burndown, which is tied to specific, time-bound releases, the epic burndown is more flexible, adjusting its timeline based on the evolving scope and challenges of achieving a grand objective (such as expanding a business into new markets, or developing a complex multi-feature product).
As Pham aptly points out, “Selecting the right chart depends on the stage your project is in and what you aim to achieve. A sprint chart is essential for daily tasks, a release chart helps you zoom out to see multiple sprints, and an epic chart offers a high-level view of substantial objectives. What matters is choosing the chart that aligns with your current focus and adapting as your goals shift.”
The role of burndown charts in different project management methodologies
Acting as a versatile and unifying tool across various project management methodologies, burndown charts, and their utility, extend beyond a single framework. Whether tracking the urgency of a sprint in daily Scrum or the flow of tasks in Kanban, these charts provide a visual language that articulates efficiency, alignment with project goals, and adaptability to changing conditions. Here's how:
Scrum: In Scrum, a burndown chart is vital in project planning and tracking. It helps visualize the work remaining in a sprint, fostering a sense of urgency and a focus on completion. Sprint burndown charts become a daily touchpoint for team members, offering transparency and goal/task alignment.
Kanban: A burndown chart is still desirable despite Kanban's flow-based methodology, where tasks flow from one stage to another. It can monitor progress over specific time frames, providing insights into how work is flowing and where bottlenecks may occur.
Lean: Lean is about maximizing value while minimizing waste, and the burndown chart aligns with this philosophy. By providing a clear view of remaining work versus time, they facilitate the identification of wasted resources and promote a continuous improvement mindset.
As per Pham, the brilliance of burndown charts lies in their simplicity and universal applicability. Whether you're engrossed in Scrum or adapting to Kanban's flexible nature, these charts distill complex workflows into easily understandable visuals. This clear representation not only helps in bridging communication gaps but also instills a proactive mindset, which is the key to any successful project.
What are the pros and cons of using burndown charts?
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of burndown charts can help you decide when and how to use them effectively. Here's a side-by-side comparison to help you understand the pros and cons of burndown charts:
Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
Visual clarity | Provides a clear, visual representation of project progress, making it easy to stay on track. | May oversimplify complex projects, leading to misunderstandings or overlooked details. |
Real-time tracking | Offers real-time insights into the project's state, enabling quick decisions. | Can become misleading if not updated regularly or if the initial estimates are inaccurate. |
Collaboration and alignment | Fosters collaboration by creating a common reference point for all team members. | May not reflect non-quantifiable aspects of the project, such as quality or interpersonal dynamics. |
Adaptability | Adaptable to different project management methodologies, providing a universal tracking tool. | Its effectiveness can be limited in projects where the work isn't easily quantified or broken down into discrete tasks. |
Navigate your next project with precision
“Just as you wouldn’t use a hammer to tighten a screw, the choice to use a burndown chart must be context-driven,” says Pham. It's evident that every tool has its optimal application. And while the burndown chart is a powerhouse in many scenarios, its effectiveness hinges on the project's nature and context.
For instance, burndown charts are most effective in projects that follow Agile methodologies or have time-bound goals, less so in more exploratory or research-based projects where timelines are not the primary concern.
Time to apply what you've learned for future success:
Assess the context: Before diving headfirst into using a burndown chart, consider the dynamics of your project. Is it fluid and fast-changing, or does it have a more predictable trajectory? If your project has a predictable trajectory, a burndown chart can offer precise day-to-day tracking and foster a strong sense of accountability. On the other hand, if your project is more fluid, you might need to adjust your burndown chart more frequently to reflect changing priorities and tasks.
Educate your team: Ensure every member understands the principles and the purpose behind the burndown chart. A tool is only as effective as the hands that wield it.
Go with iterative improvements: Reflect on your projects, consider their dynamics, and gauge when the burndown chart will be your ally. Challenge yourself: On your next project, apply the burndown chart strategically, and note its impact on team alignment and decision-making.
Your path to becoming a more adept project manager gets paved with every informed choice you make.