Three emerging cybersecurity trends your small business should adopt to level up defense against evolving cyberattacks.
The cybersecurity industry is continuously evolving. As a small-business owner or security leader, if you want to stay ahead of or keep up with the latest cybersecurity trends, you’ve come to the right place.
In this article, we've got the inside scoop on three security trends that are set to drive the future of cybersecurity, based on forecasts by leading global IT research firm Gartner.
Equipped with this information, you and your security team will be in a better position to adapt your small business’s existing cyber defense strategies for future needs and protect your business resources from hackers and cybercriminals.
Our lists of IT Services Agencies by location can help you find the services you’re looking for.

1. Increasing adoption of insider risk management programs
According to Gartner's 2023 cybersecurity predictions[1], 50% of midsize businesses will adopt a formal program to manage insider risk by 2025, up from 10% today. That’s because employee error or negligence is a major cause of cybersecurity failure.
Our 2022 Healthcare Data Security Survey* reports that more than one-third of medical practices have experienced a data breach, of which 49% was caused by human error. This suggests that even the strongest cybersecurity programs can be compromised if human threat actors unintentionally make mistakes or maliciously compromise their organization’s resources.
To combat insider threats, half of the security leaders from midsize businesses are expected to adopt formal insider risk management programs by 2025, with a focus on early detection and prevention of data exfiltration[1].
Gartner[1] recommends the following tactics to help build your insider threat management program:
Train your employees. Link the importance of cybersecurity to your business success, and update your security training to focus on insider risk prevention. Conduct immediate corrective sessions whenever someone violates a policy. According to our 2022 Security Awareness Survey**, 53% of small businesses provide security training more than once a year.
Get support from leaders and other teams. To make your insider risk program successful, you need support from senior leadership as well as HR and legal teams. Without help from HR and legal, it’ll be hard to hold everyone accountable.
Roll out the program one step at a time. Don't make too many changes too fast; Instead, take a phased approach to implementation. This way, you can reach your goals without hampering your operations or burdening your employees.
Use tech tools to strengthen your insider risk program. You can use different software tools to build your program: data loss prevention tools, risk management tools, access governance tools, employee training tools, and more. The exact tools you need will depend on how comprehensive you want your program to be.
2. Zero trust to become the starting point of business security
Zero trust is a security strategy that explicitly authenticates users (both internal and external) and allows them just the right amount of authorization to access business resources. Gartner forecasts that by 2025, 60% of organizations will embrace zero trust as the first step to enterprise security[2].
Zero trust doesn’t mean no trust, but access to resources in this security strategy is always verified, regardless of whether the user is an insider or outsider to the organization. For instance, you wouldn't let anyone enter your office without verifying their identity, right? Zero trust uses the same concept for your digital assets.
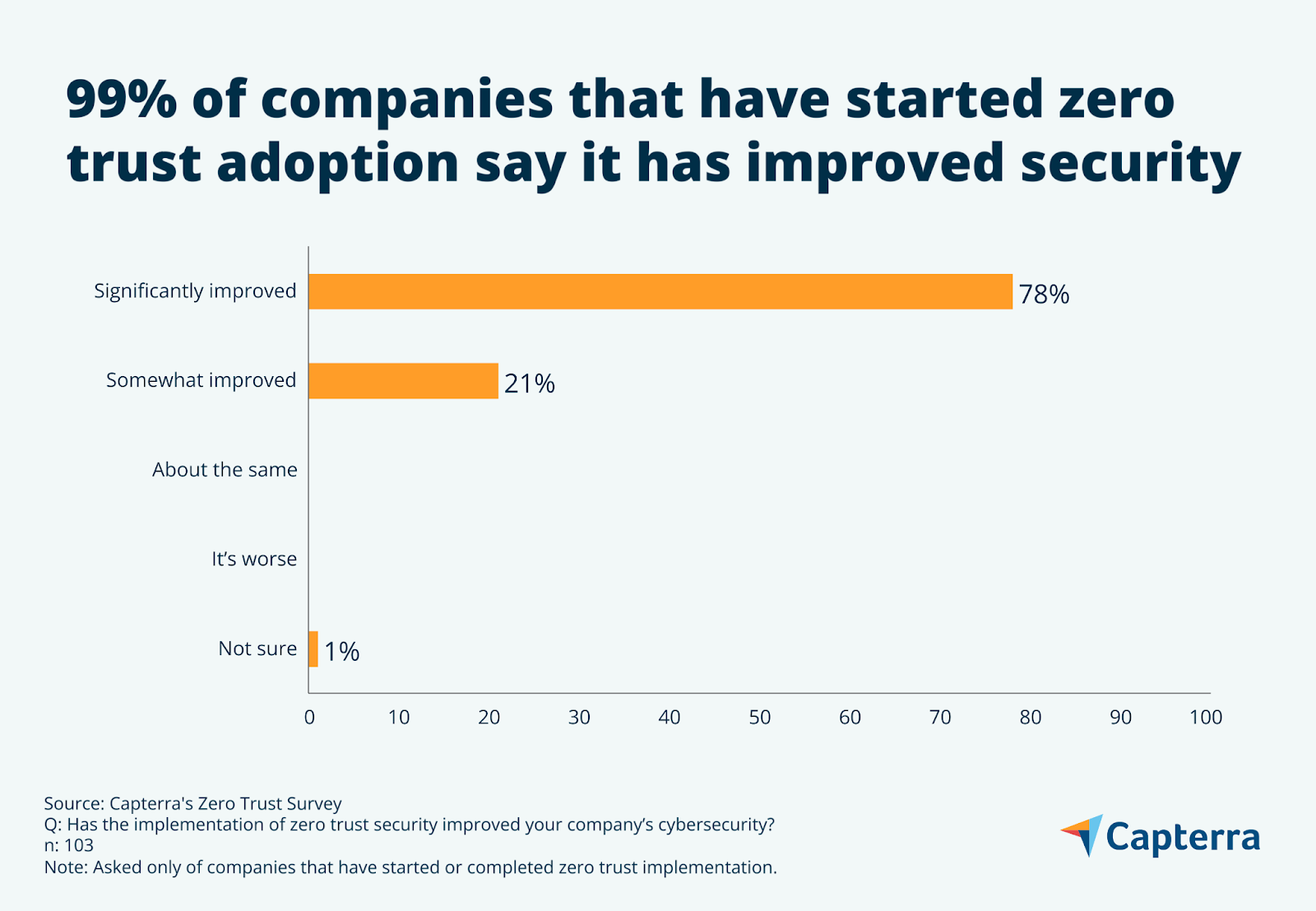
Forty-four percent of businesses that participated in our 2022 Zero Trust Survey*** have already started zero trust implementation, and another 40% plan to adopt it at some point in the future—only 16% have not considered or decided against it. Of those planning future adoption, 72% intend to begin implementation within the next year.
/ Did you know?
Zero trust strategies are recommended by government organizations such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)[3] and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)[4]. They are now also being mandated for federal agencies as part of President Biden’s move to improve the nation’s cybersecurity[5].
We recommend the following tips to adopt zero trust for your small business:
Prioritize your security efforts by determining your most valuable assets and data based on their potential impact on business operations if they were compromised.
- Add an extra layer of security by implementing multifactor authentication (MFA)A security process that requires more than one method of authentication from separate categories of authentication methods to verify a user's identity.for all remote access to your systems and networks.
Regularly review your security policies and procedures, including access controls and monitoring for unusual activity, to ensure they align with zero trust principles[6]. Also, ensure your employees are trained on these policies and procedures.
3. Use of cybersecurity mesh for a more consistent security posture
According to Gartner[7], the adoption of a consolidated cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA) is increasingly gaining popularity due to the technology’s ability to offer a common, integrated security structure to secure cloud, data center, and on-premise assets.
A cybersecurity mesh connects different security tools to share information and work together to protect your small business, leading to enhanced detection, efficient responses, consistent security policy, granular access control, and better overall security. It helps eliminate siloed approaches to security and identity management architectures and facilitates zero trust adoption.
Businesses that adopt CSMA by 2024 can reduce the financial impact of individual security incidents, such as malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks, by an average of 90%[7].
Gartner[8] recommends the tips below to adopt CSMA for your small business:
Carefully select security tools based on their ability to integrate with your current setup and built-in features to meet your specific cybersecurity needs.
To have a comprehensive long-term security plan, invest in the four main areas CSMA covers: analyzing and collecting information about threats, managing access to your systems, having consistent security policies, and keeping track of your security progress.
Invest in technologies such as security information and event management (SIEM) and threat intelligence that use data analysis to help you stay ahead of emerging threats and improve your cybersecurity posture.
To quickly get started with CSMA, use all-in-one cybersecurity platforms that can simultaneously handle multiple tasks. To select your best fit, check out Capterra Shortlist for cybersecurity software.
Ready to embrace the future of cybersecurity?
You can’t improve cyber defense against evolving threats without making cyber security a part of your company’s culture. To help you out, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recommends adopting a "just culture" approach[9].
As per this approach, you should prioritize open and positive communication with employees, allowing them to report any concerns without fear of punishment. By creating a culture of security where everyone understands their role in maintaining security, you encourage your staff to bring their best value to your small business.
Once this culture is established, you can then consider incorporating newer technologies to stay ahead of the constantly changing threat landscape.
Additional resources to help you learn more about improving cybersecurity for your small business:

