Biometrics allows your small business to move beyond complex or weak passwords.
About 35% of IT managers from a 2022 Capterra survey* blame poor passwords and weak logins for cyberattacks on their business. One way to avoid this challenge is to consider biometric authentication instead.
But is this tech feasible for your small business? Although 39% of small-business leaders already use biometric authentication to secure their apps and devices per our 2022 Passwordless Authentication Survey**, ensuring your employees trust you with their biometric data and that your company has enough budget to power this security system properly is essential.
Ahead, we share more on biometric authentication—what it is, how it works, how your peer small businesses leverage it, how to deal with its challenges and top myths about this security tech.
What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is a passwordless security technology that scans unique biological identifiers, such as fingerprint, voice, face, or iris, to ensure people are who they claim to be. When a user tries to log in, the tech compares the authenticated scans stored in its database with the user’s actual physical traits to provide access. For instance, when you unlock your phone using your fingerprint, you authenticate yourself via biometrics.
However, not mixing up biometric authentication with biometric identification is important. While both involve using unique biological traits, the latter is more like a search mission rather than just a lock-and-key mechanism. For instance, a facial recognition system at an airport scans faces to identify individuals on a watchlist. The system searches through an array of faces instead of simply verifying one.
Ready to hire IT services for your business needs? Browse our list of companies in the following areas:
Different biometric authentication methods
Each type of biometric authentication offers a distinct combination of security and accessibility. These four are the most common variants:
Face scan: It captures unique facial features, such as eye spacing and cheekbone shape, to create a mathematical model of your face. This model is then stored and matched with future scans for authentication. Especially practical for businesses that handle sensitive information, it can be implemented through office cameras or built-in webcams on laptops. Since it doesn’t require expensive hardware, face scanning is an affordable biometric authentication method compared to others.
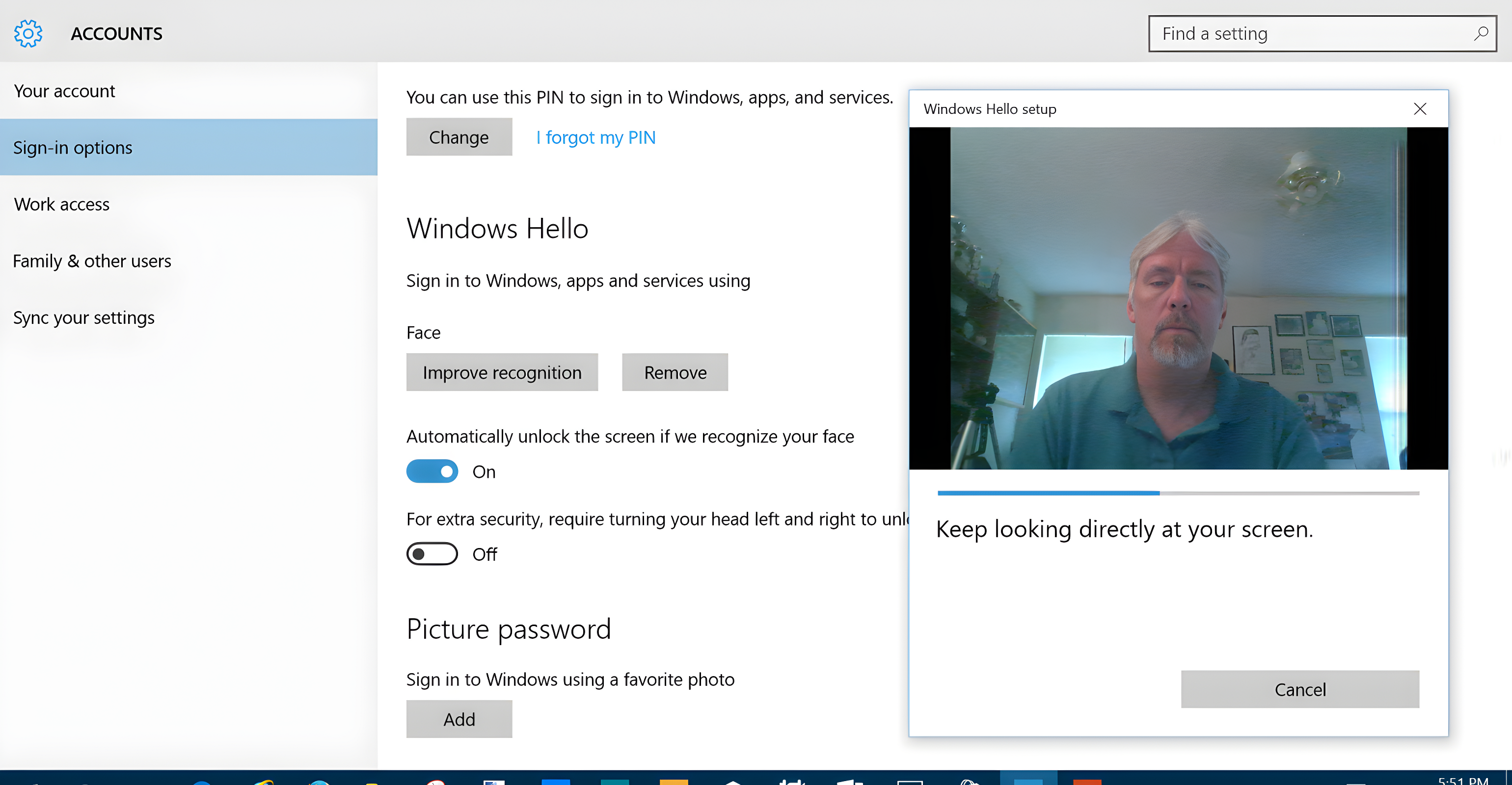
Face authentication in Microsoft’s Hello security in Windows computers[1]
Fingerprint scan: This biometric authentication technology recognizes the unique patterns on your fingertips and matches them with stored prints. It’s versatile and can secure various assets, from office doors and safes to computers. Although it involves an initial investment in hardware such as fingerprint scanners, this method can provide enhanced security depending on your specific needs.
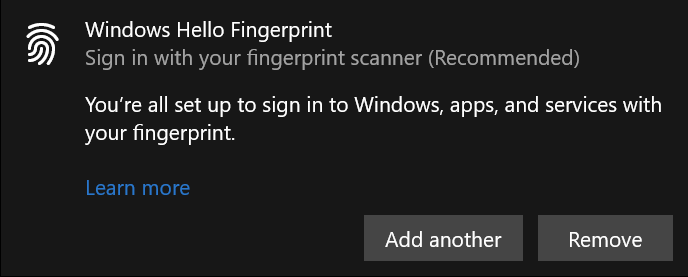
Fingerprint scanning in Microsoft’s Hello security in Windows laptops (screenshot taken by the author)
Voice scan: This method authenticates a speaker by analyzing and matching unique voice features, such as pitch, tone, and rhythm, with a prerecorded sample. It’s especially useful in industries such as customer service, where identity verification over calls is crucial. Since voice recognition software can be installed on existing hardware, it could be a cost-effective and readily accessible security option.

Iris scan: This authentication method detects the unique patterns of your iris. It first locates your pupil’s position, eliminates unnecessary elements such as eyelids and eyelashes, and then clips out only the iris part. After that, it matches your iris patterns with the stored scans to verify your identity. Due to its exceptional accuracy, iris scanning is suitable for government agencies, financial institutions, or organizations that need to secure extremely high-risk areas or sensitive data. However, this method involves substantial investment in iris recognition hardware.
Benefits of biometric authentication for your small business
Biometric authentication systems have been a game-changer for many small businesses. Let’s read what your fellow SMB owners say about this technology's impact.
Seamless operations and improved security
Teresha Aird[2], the co-founder of an online B2B real estate brokerage firm, shares how biometric verification has transformed her business operations:
“Ever since we incorporated biometrics, operations have run smoother. The hassles of lost keys and forgotten passwords vanished, and unauthorized access became a thing of the past. Our security level soared with a layer that’s challenging to breach. Plus, attendance tracking with fingerprints became so much easier.”


Teresha Aird
Co-founder of Prime Office Space
Faster resource onboarding with facial recognition
David Ciccarelli[3], a tech entrepreneur who runs an online voice-over service platform, explains how biometrics have drastically improved onboarding for his organization:
“Instead of the cumbersome traditional process, we now leverage facial recognition for secure and swift remote onboarding and data access. Just a quick scan of a new employee’s face using their device’s camera, and voila! Their identity is verified. This method has been very helpful for us, especially in this era of remote work.”


David Ciccarelli
CEO of Voices.com
Easier fraud detection and better customer satisfaction
Next up is Billy Parker[4], director of a UK-based gift delivery eCommerce website. Parker shares how biometrics turned things around for his business:
“With biometric authentication, we saw real improvements in our daily tasks and overall security. Customers felt safer shopping with us, which bumped up their satisfaction. There was a sharp drop in fraudulent activities, probably because tricking biometrics isn’t that easy. We use it mainly to verify customer identities during transactions, making it harder for fraudsters to make purchases.”


Billy Parker
Managing director at Gift Delivery UK
Risks associated with biometric authentication
Although biometric authentication technology ensures more robust security, it comes with its own hurdles. Here’s what business leaders we surveyed** have shared about their concerns.

Reduced privacy
A biometric authentication system stores highly personal data, raising questions about how this information is stored, used, and protected. Address these privacy concerns by transparently communicating your data handling policies, implementing strict security protocols, and providing your employees and customers the choice to opt-out.
Interestingly, most (84%) of our survey** respondents trust their employers with their biometric data. Yet, 85% feel that employers’ use of this data should be controlled by law. Additionally, 85% of respondents think consumers should have the right to opt out of facial recognition technology used by private companies. This sentiment underscores the need for clear biometric data usage and privacy regulations.
Risk of data breaches
While biometric data is secure, it’s not invincible. Breaches can happen; when they do, the consequences are more severe than losing a password. Therefore, you must invest in robust cybersecurity measures such as encryption and firewalls to protect biometric data.
Data misuse and identity thefts
Biometric verification data is inherently personal, making it a potential target for malicious activities such as identity theft. The repercussions of such activities include reputational damage for businesses and a breach of trust for customers. Regular audits of data access controls and the implementation of stringent data usage policies can help your small business mitigate these risks.
Chances of inaccuracy and bias
Even though biometric authentication technology is super accurate, sometimes it might mess up. This can happen due to bad lighting or the tech being biased. Brad Banias[5], a legal advisor for small businesses, says:
“There’s a problem when some employees can’t use the biometric system. Maybe they have a physical disability. That’s why having a backup way to get in is important.”


Brad Banias
Federal court immigration lawyer
Brad’s making an important point: Technology has to work for everyone, so any biometric system you use must be fair to all users, even those with physical disabilities. Also, it’s crucial to tackle any racial bias in tech.

He adds, "You must find the right balance between keeping things secure and respecting user privacy when using biometric tech. To achieve this, consider measures such as storing data locally instead of on the cloud, implementing strong encryption, and informing users exactly what data is collected and why.”
Myths about biometric authentication
Despite being one of the most secure user authentication methods, biometric technology is still a question for many people, giving birth to many myths, some of which we’ve debunked below.
1. Biometric technology keeps a copy of your images or prints
That’s false. Whether facial or fingerprint scanning, biometric technology doesn’t store your image or prints. Instead, it converts data related to your unique biological features into a mathematical model, then stores it in the database. So, no photographic image or literal fingerprint is sitting around that could compromise your privacy.

Face recognition through a mathematical model of a user’s face, not a picture[6]
2. Biometric models expire as users age or their features change
That’s inaccurate because modern biometric models carefully record changes in user appearance with regular usage. These systems update the stored mathematical representations to reflect regular feature changes, ensuring accurate user authentication.
And in case of significant changes, the system prompts users for additional authentication, such as a PIN code or security question, and then resets the recorded scans. This multimodal authentication approach enhances security and ensures the system remains robust despite dramatic changes.
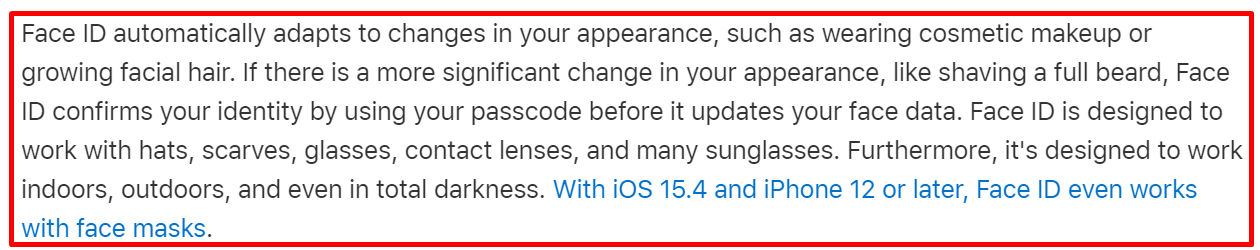
Apple’s official Face ID support documentation[7]
3. Static images can fool biometric authentication
That’s an outdated concern. Modern biometric technologies, like those in current smartphones, are much smarter. For face scans, they use true depth technology that maps the geometry of your face, looking for signs of movement such as blinking eyes to ensure a live person is in front of the camera.
The sensors can detect blood flow for fingerprints, ruling out the possibility of a fake print. Voice scans also use algorithms that differentiate between a live voice and a recorded one. The chances of being fooled by a static image or a recording are significantly low.

Apple’s official Face ID advanced technology documentation[7]
Biometric tech is a strong security choice, but mind the precautions
If you’re all set to embrace a biometric authentication tool in your small-business operations and are thinking of starting discussions with stakeholders, here are a few key considerations to make:

Check out these additional resources on authentication:

