Plan for when and how your business could use AI technology with this primer.
According to the 2022 Gartner Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence[1], AI-powered technology is expected to hit mainstream adoption in two to five years. For small-business leaders like you, this means you’ll want to start planning how and when you’ll get on board.
To help, we'll walk you through some important AI technology terms and industry-specific use cases supported by insights from Gartner research. We'll also share findings from surveys we've run showing how your peers are investing in AI tools or services so you can benchmark your own efforts.
/ What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability to replicate human intelligence with technology. AI technology enables machines to think, learn, make decisions, and adapt to their environment. Examples of AI include self-driving cars, virtual booking agents, chatbots, smart assistants, and manufacturing robots.
Artificial intelligence terms to know
Before we get into how AI works, let’s break down some terms you’ll encounter in this and other discussions about AI. Many of these terms can be found in Capterra’s glossary, provided to help you navigate any business or software-related jargon that may pop up in the topics we cover.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that mimics the human brain by clustering data and making predictions. It eliminates the data labeling and processing that supervised machine learning algorithms require. One example is self-driving cars, which operate and make decisions based on unlabeled and unpredictable variables, such as a pedestrian in the road.
Machine learning (ML)
Machine learning systems use AI and deep learning techniques to extract insights from data and create logical data models. The data models are utilized in business processes to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. A machine learning algorithm can be used to build self-driving cars, product recommendation systems, and language translation systems.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing enables computers to understand human language. Computers do so by analyzing text and extracting meaning from it to perform tasks such as translating languages and understanding questions posed in natural language.
Neural network
Another subset of ML, a neural network allows machines to mimic the human brain through algorithms that enable pattern recognition and problem solving. Similar to how a human makes decisions based on available information, a neural network processes labeled data in ways that allow it to recognize faces, search for flights, or even build a menu for Thanksgiving dinner[2].
Supervised learning
Supervised learning is an approach to machine learning where an external party (e.g., a human) provides labeled data to the ML model. Tagged photos on social media are one example of supervised learning; the machine learns image recognition based on the user’s tagging history.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning is another approach to machine learning where no labels are provided. Unsupervised learning is useful for pattern recognition and anomaly detection. For example, if an unsupervised learning AI algorithm is provided with images of cats and dogs without those images being labeled as such, it will learn the differences based on their features.
Virtual assistant (VA)
A virtual assistant is a digital program that understands voice commands and natural language to perform tasks for a business. It executes tasks that, previously, only humans could complete. VAs use semantic and deep learning technologies such as personalization, prediction models, deep neural networks (DNNs), and natural language processing.
Businesses might invest in a VA to complete tasks typically performed by a human personal assistant, customer assistant, or employee assistant. These tasks could include responding to customer queries, handling financial transactions, and setting up important meetings with clients or potential investors.
Find the right AI company for your business in Capterra’s list of artificial intelligence companies in the United States.
How does AI work?
Artificial intelligence works by applying logic-based techniques, including machine learning, to interpret events, automate tasks, and complete actions with limited human intervention. The analysis and techniques are used to build data models with fast and iterative processing that are fed into machines via software to act like humans.
Here are the three different types of AI techniques that can be used for machine training to accomplish tasks.
Reactive machines: The simplest type of AI that is used to perform basic operations such as input and output data. The machines focus on live observations to perform tasks instead of relying on pre-planned data models.
Limited memory: This type of AI possesses the ability to store and analyze data for better decision-making. Limited memory AI learns from historical data to make future predictions and perform tasks.
Theory of mind: The type of AI that imitates the human mind to understand emotions and perceive thoughts. It possesses the ability to analyze data and learn and adapt to its environment for better predictions and task performance.
What does AI adoption look like for a small business?
AI adoption is more common in some areas or industries than others. These include customer service, healthcare, construction, and HR. Industries that use AI often have processes that are better suited for machines than humans for reasons of big dataBusinesses may also be interested in AI solutions if they have a need for trend prediction or forecasting, such as in finance or real estate. Whatever their reason for AI adoption, businesses typically go with one of two options: investing in AI tools or AI-as-a-service.
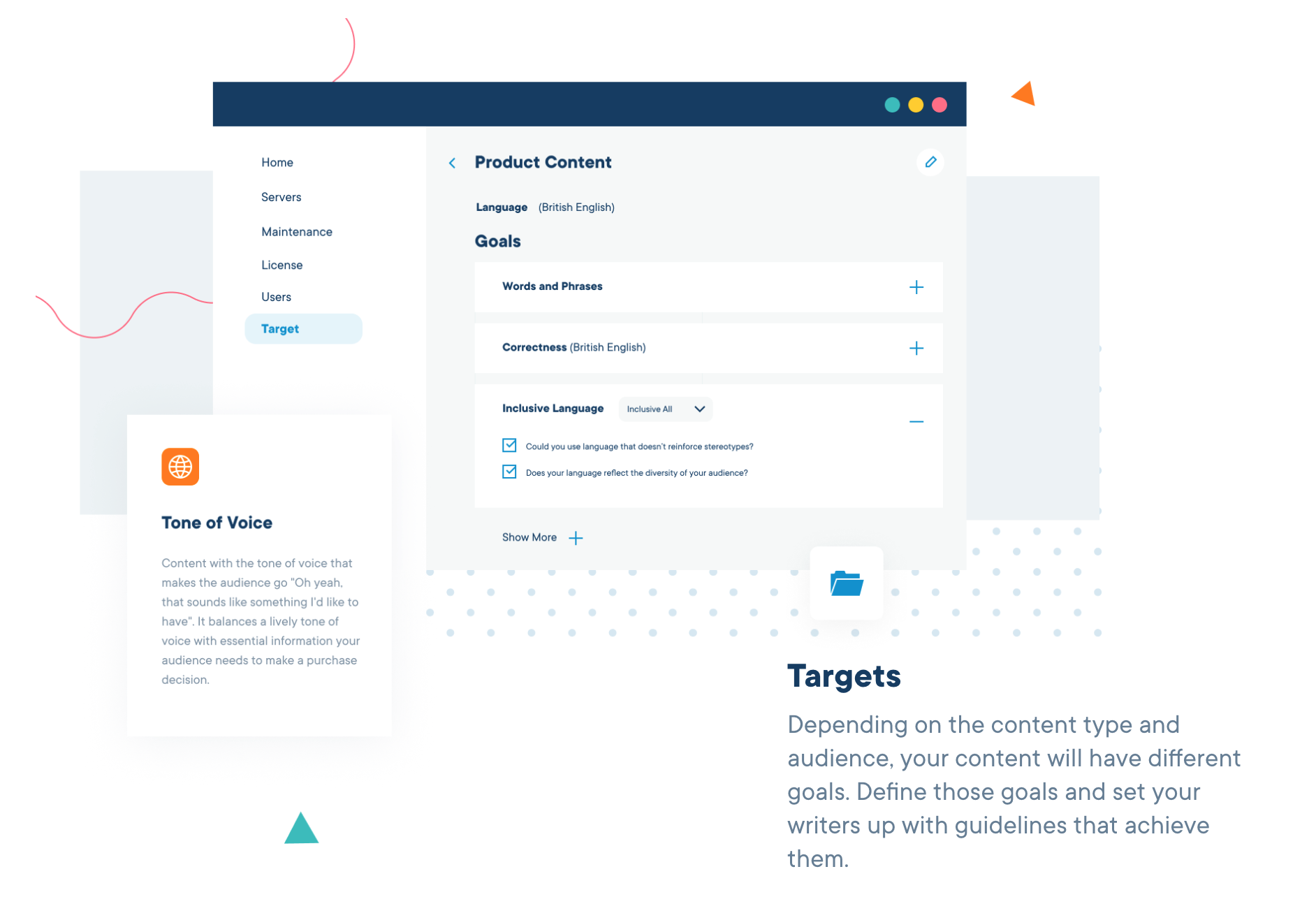
Image of AI application Acrolinx
Artificial intelligence tools, such as the example shown above, mimic human behavior and learning patterns. They can be used in a variety of business areas, from customer service and sales to data analysis and task automation. Benefits of AI tools include faster, more accurate data analysis, improved customer experience, and more time to spend on higher-value tasks.
Depending on your budget, as well as your ability to process and analyze the data brought in by an AI tool, you may elect to invest in AI-as-a-service (AIaaS) instead by hiring an AI company, like 28% of SMB leaders did in the past 18 months according to a recent Capterra survey [*]. AIaaS allows businesses to leverage the capabilities of AI through cloud computing models.

When you invest in AIaaS, you are bringing on a third party to automate processes such as setting workflow, aligning tasks, and capturing customer and client data. AI services companies can also strategize, implement, and develop software solutions through AI techniques, and may also offer additional services such as data governance, security, audit, and monitoring.
By offering AIaaS, companies transform AI technology into tangible solutions for your business. AI services companies often offer their own software as solutions to business problems. These AI solutions are developed by a data scientist, analyst, and/or engineer based on the analysis of business challenges and goals, and may include a machine learning model, NLP, and/or VAs. Below is a brief video that describes the pros and cons of AIaaS.
What are some ways AI can help my small business?
Below, we’ll cover three industry-specific use cases so you can get a better sense of how AI can help your small business:
Improve customer experience with chatbots and VAs
A chatbot is an AI-enabled program that can help customer service agents by simulating human conversations through a chat interface. Usually appearing on websites and mobile apps, they simulate the experience of customers talking to sales reps. However, chatbots are simply responding to a script. They use the script to determine how to assist a customer in need.
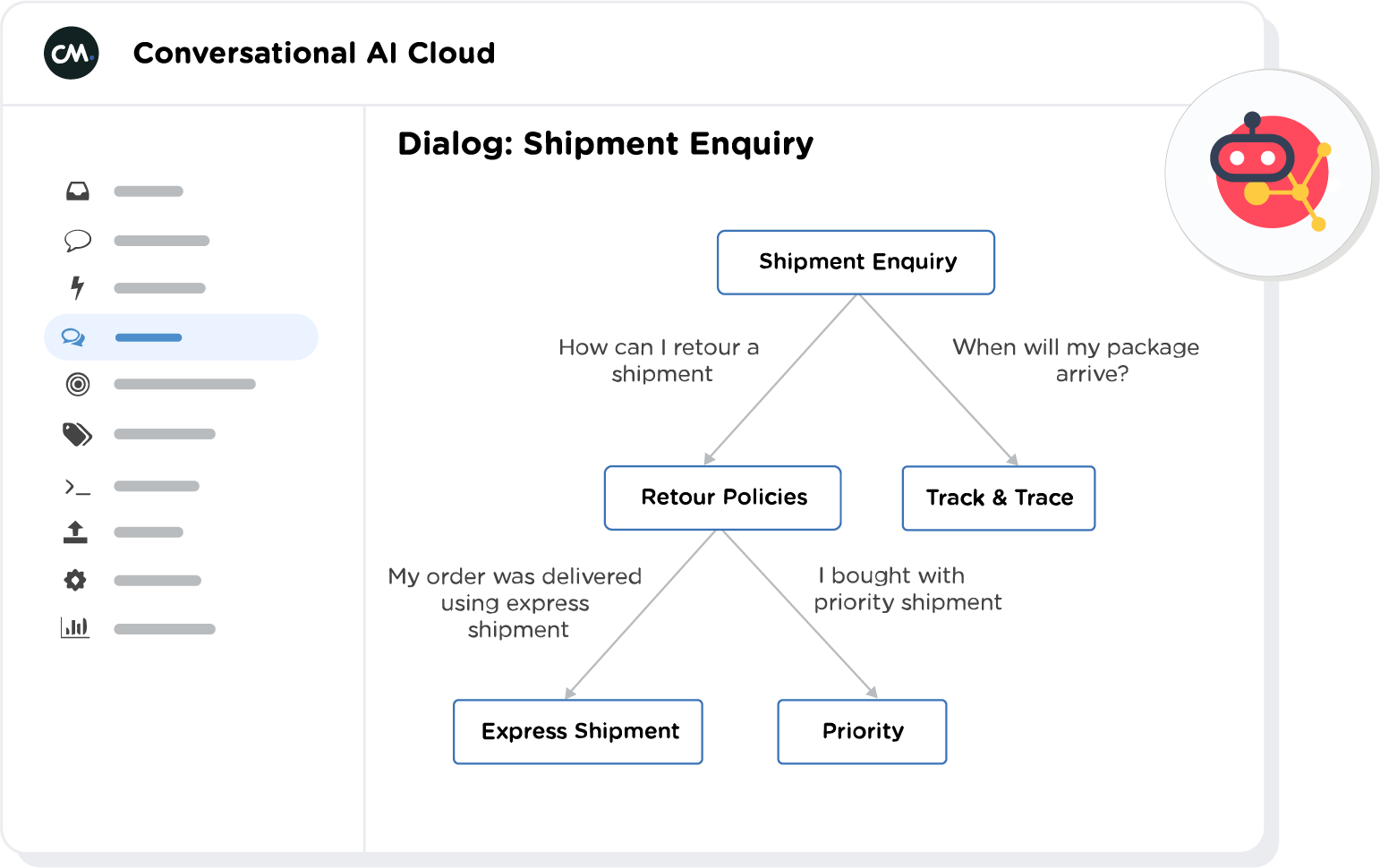
Image of chatbot software platform Conversational AI Cloud
The AI chatbot is great for simple tasks, such as the following:
Answering customers’ most frequently asked questions (FAQs).
Queueing a human customer service agent for questions that fall outside the FAQs, or for requests that need to be escalated.
Assisting a customer who is having trouble logging into their account.
Scheduling appointments, if linked to a calendar.
Collecting details such as business needs before passing a customer to sales.
In sum, chatbots are extremely useful for tasks that involve gathering and forwarding information, and they provide relief for service reps who might feel like bots themselves due to answering the same questions again and again. They also free up those same agents to assist customers with more complicated questions, or to work on higher-value tasks.
If your customer service team spends a lot of time assisting customers with any of the above, we recommend that you start with a chatbot. When you’re ready for more advanced AI capabilities—or if you’re trying to build a business case for AI system adoption that considers what the next five to ten years will look like—we recommend the virtual assistant.
/ Capterra tools and tips
While both chatbots and VAs are used to enhance customer service, VA capabilities are broader than chatbots’. Virtual assistant software helps businesses conduct personalized conversations with users and automate tasks or business processes with/without human assistance, such as:
Communicating with customers in ways that feel more natural and less scripted, otherwise known as conversational AI[3].
Observing behaviors, such as when and what customers tend to purchase.
Building and maintaining data models, such as trend cycles.
Predicting and recommending actions, such as when to increase or decrease production.
Give your marketing team the upper hand with AI copywriting software
In order to improve SEO and attract leads, your marketing team needs to produce new content quickly and continuously. And if your small business has limited resources, that’s no small task.
AI copywriting software can give your team the upper hand by generating content in just minutes, and it doesn’t mean skimping on quality. According to another Capterra survey[**], 82% of marketers say that AI-generated copy is just as good as what humans can write, if not better.

Other perks of using AI for copywriting include:
No substantial learning curve: 57% of marketers say it took their company less than six months to learn how to use AI or ML technology.
More room in your budget and schedule: 88% of marketers find that AI or ML software saves their company time and money.
Straightforward content: Almost half (49%) of marketers say AI or ML software is very successful at producing clear or easy-to-read content.
AI copywriting isn’t a fix-all, however. Keep these recommendations in mind:
Have realistic expectations for implementation. 69% of marketers say it took their company 6+ months to implement AI or ML technology.
Develop a data management or risk mitigation plan. 35% of marketers cite risk and data management issues as top challenges of using the technology.
Train your team to check AI-generated copy for accuracy. A third (33%) of marketers rated AI copywriting software the least successful when it comes to providing accurate or error-free content.
Streamline your hiring efforts with AI-powered recruitment tools
Anyone who has ever sat through a job interview would agree that there are some aspects of the recruiting and hiring process that are best completed by humans. A machine can’t provide a reassuring smile or handshake, nor can it empathize with personal experiences.
What artificial intelligence can do is make recruiting and hiring a less time-consuming process for your small business by managing interview scheduling, screening application materials for keywords, and assisting with applicant tracking.
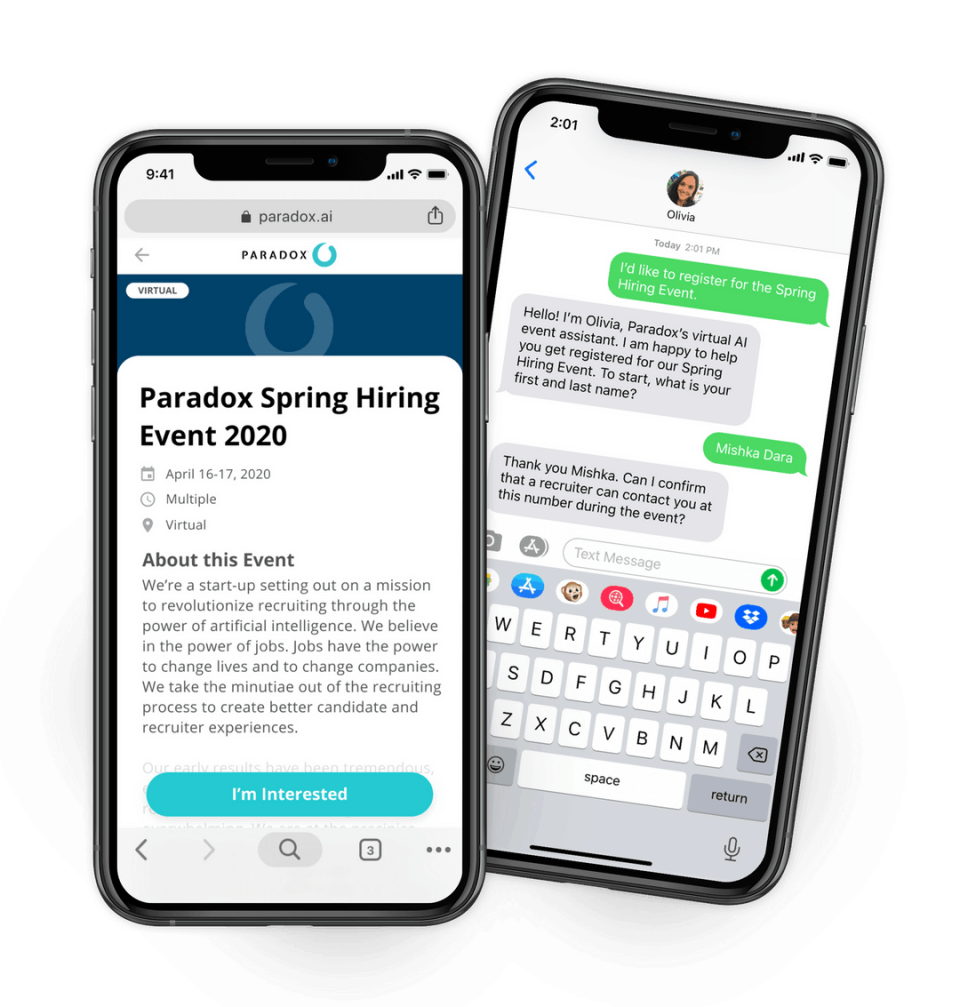
Image from AI recruiting tool Olivia
AI can also help eliminate bias in hiring practices. Something to be aware of, however, is AI bias [1], a data-labeling problem that may inadvertently pose a disadvantage to diverse candidates.According to Forbes[4], one of the most infamous AI ethics breaches occurred in 2018, when Amazon discovered that its ML-based recruitment program was biased against women.
AI bias can also occur with an AI system that searches for candidates by geography, which can inadvertently produce racially biased outcomes. To avoid AI bias, the onus is on both the vendors building AI-based hiring platforms as well as the companies using them to assess whether hiring outcomes are more equitable.
Putting together your AI investment plan
Now that you’re familiar with the basics of artificial intelligence and how it can help your small business, you’ll first need to decide whether you’re ready to invest in an AI solution. At your next leadership meeting, ask the following questions to determine whether you’re ready for AI now or within the next five to 10 years:
Are we due for a software upgrade or new technology altogether?
Are we in an industry where AI adoption makes sense?
Do we have the proper staffing in place to research and implement new technology?
If your team decides it is ready to invest in an AI system, keep these recommendations in mind:
Create a shortlist of use cases that demonstrate why an AI solution is appropriate for your small business, and gather some data for them.
Choose the AI solution that’s the best fit for your use cases, data, and skill level.
Ensure that you have staff who understands and can implement the AI program you’ve selected. If not, consult a third-party organization.
Note: The screenshots of applications selected in this article are examples to show a feature in context and are not intended as endorsements or recommendations.
