Today’s HR leaders oversee a wide range of responsibilities. From essential tasks like making sure that workers get paid on time to more complicated initiatives that help their organization prepare for the future, the role of modern HR departments is critical for business success.
Whether you’re an experienced Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO) or a new HR associate, the insights packed into this guide will help you brush up your knowledge of this critical business function. Ahead, we’ve collected an assortment of information and resources on all things HR, from the foundational duties of a typical department to the latest technology and trends defining the future of human resources.
What is human resources (HR)?
Human resources is a business function responsible for supporting the ongoing recruitment, development, and management of talent. Historically, the purpose of an HR department was to compensate and administer benefits to the workforce as well as ensure compliance with employment laws. However, today’s HR departments go beyond this by taking on more strategic tasks that help organizations stay competitive and resilient (such as succession planning and employee development).
Foundational HR Content




Why is human resources important?
A strong human resources function is a critical part of any organization for the following reasons:
1. HR is responsible for talent acquisition
HR shapes the future of an organization by attracting and recruiting high-quality talent to it. They have to ensure that the right fit is hired for the right role as well as create an onboarding process where new hires feel supported from day one.
2. HR oversees employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity
HR is tasked with tracking and improving metrics that impact business outcomes such as talent retention and productivity. They achieve this by carrying out different initiatives, whether it be introducing a formal performance review process or mapping out potential career paths for different departments.
3. HR takes the lead in cultivating a positive work culture
Promoting and communicating what’s unique about an employer’s brand is one aspect of a mature recruiting strategy. Because of this, HR is often tasked with setting the tone for their organization’s company culture. There are many ways they accomplish this; for example, they may introduce diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives or encourage executives to sponsor employee resource groups (ERGs).
Key responsibilities, roles, and functions of HR
The full range of responsibilities for a modern HR department depends on the size and maturity of the organization they’re supporting. With that in mind, we’ve identified six standard areas of focus for a typical HR department:

Employee compensation and benefits
One of HR’s most important duties is to develop and manage compensation plans for employees. Compensation plans include information about what an employee is paid to do, how and when they will be paid (such as hourly, salary, etc.), and to what extent their pay is related to their performance. Typically, compensation management is accomplished through a payroll system like the top-rated examples featured here.
Benefits administration is another aspect of employee compensation that’s managed by HR. Employee benefits often include things like health insurance, retirement and pension plans, and paid leave. HR professionals work with different providers to manage benefit plan options, which employees can enroll in via a benefits administration platform. According to Capterra’s Employee Benefits Survey, a majority of HR leaders (57%) say employee benefits are extremely important to retaining top talent. Among large businesses (1,001+ employees), that number jumps to 67%.*
See more Compensation and Benefits Guides



Ensuring compliance
HR compliance refers to the process of developing policies and procedures that help businesses abide by labor laws and employment regulations. Failing to comply with local and federal laws can result in fines, penalties, and even lawsuits—meaning HR leaders have a lot of pressure on them to make sure workplace policies align with relevant regulations.
There are four main types of HR compliance:
Statutory compliance: Any government legislation related to employment (such as minimum wage laws or working age requirements) falls under statutory compliance.
Regulatory compliance: This kind of compliance is dictated by various regulatory agencies. For example, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) all have different laws that may apply to a business.
Contractual compliance: Contractual compliance is specific to a business, its employees, and any partnering organizations.
Union law compliance: If a company employs union workers, they are required to adhere to the rules set by the union.
Recruiting talent
From attracting talent to the organization to sending offer letters to candidates, every stage of the recruitment process is managed by HR. When an organization has an open role to fill, recruiters within the HR department take on this responsibility. They draft and publish job listings, source and screen candidates, and schedule interviews. In smaller organizations, recruiting may be handled by a single hiring manager or recruiter, while larger organizations typically have entire teams dedicated to recruiting.
Read more on Recruiting



Talent development: Upskilling, training, and developing employees
Talent development—which encompasses any initiatives that support employees’ learning and growth—is another area of focus for HR. There are two goals for talent development: First, to help the workforce gain the skills needed to accomplish business goals, and second, to improve the employee experience by providing individuals with opportunities that align with their personal career goals.
Learning management systems (LMS) and eLearning authoring tools are frequently used to support development initiatives. Some LMS platforms come with pre-built course libraries that employees can use to access learning materials on demand; in other cases, training specialists use these platforms to build their own custom courses.
ON THE TOPIC OF TALENT DEVELOPMENT


Performance management
HR’s role in performance management is to guide the organization through a standardized process. This includes determining which performance management techniques make the most sense for the organization as well as defining what high performance looks like for different roles. Typically, team managers will work with HR to learn how to measure and deliver feedback on their reports’ performance.
One of the most common performance management approaches is to deploy a 360-degree feedback process. With this method, employees receive confidential, anonymous feedback on their performance from their managers and coworkers—usually through a 360-degree feedback platform.
RESOURCES RELATED TO PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT




Onboarding and offboarding
When employees join or leave an organization, certain tasks must be completed. Creating standardized processes for these situations is an essential HR responsibility.
In the case of onboarding, HR specialists typically collect information from new hires through forms (such as W-4s or I-9s) and share resources like employee handbooks or benefits guides. Onboarding software is frequently used to support the orientation process.
Offboarding is a little different; especially because the steps in an offboarding process vary depending on whether an employee resigned, retired, or was terminated. In most cases, the offboarding process will involve requisitioning feedback from the departing employee and providing a means for them to return any loaned equipment. In some cases, departing employees may have to sign a nondisclosure or noncompete agreement.
SEE OUR RESEARCH ON OFFBOARDING RISKS

Succession planning
As an organization grows, there’s a need to identify leaders within the workforce who have the potential to take on an executive role in the future—this is succession planning, a practice that’s commonly seen in strategic HR.
While succession planning is often associated with enterprises, small businesses and startups can benefit from this practice as well. For example, if the owner of a small business expressed a desire to retire, having a succession plan in place would help ease the transition by identifying team members qualified to fill the gaps left by their absence.
Succession planning software is often used to support this HR function. These tools are built to assist with succession planning through features like competency modeling, internal talent pools, performance dashboards, and training plans.
SEE HOW CAREER PATHING HELPS SUCCESSION PLANNING

What are some HR best practices?
Below, we’ll take a look at four HR best practices.
Ensuring fair compensation for employees
Making sure employees get paid is one of the most important responsibilities for HR. But even beyond ensuring that paychecks are delivered on time to all employees, HR is accountable for compensating employees fairly and equitably—an undertaking that’s not always as easy as it sounds.
In the United States, there is a series of legislation related to pay discrimination that HR professionals must abide by, including The Equal Pay Act (EPA), The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA), and The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Additionally, several states (such as California, Colorado, New York, and Washington) have implemented laws requiring employers to include salary information in job listings to improve pay transparency.
Many HR departments have their own strategies for improving compensation fairness amongst employees. For example, performance-based compensation is a popular approach that rewards employees who have met or surpassed their job’s requirements (usually in the form of a year-end bonus). Some HR teams may also conduct yearly pay audits to compare the salaries of those who do similar work and address any discrepancies.
If you’re interested in learning more about the latest trends in employee compensation, check out these resources:
Creating an appealing Employer Value Proposition (EVP)
Employer value proposition (EVP) refers to the aspects of a company that make it an attractive place to work. Defining and promoting an organization’s EVP is an HR best practice that supports talent acquisition efforts.
Offering competitive compensation, benefits, and perks is a must in order to have a strong EVP. It’s also a good idea to call out any unique aspects of the employee experience at your organization; for instance, highlighting ongoing DEI initiatives or existing ERGs is a good idea.
One factor that makes promoting your EVP difficult is that employees’ preferences are constantly changing. For instance, flexible work arrangements are in demand post-COVID, which caused many businesses to include mentions of hybrid or remote work opportunities in their EVP.
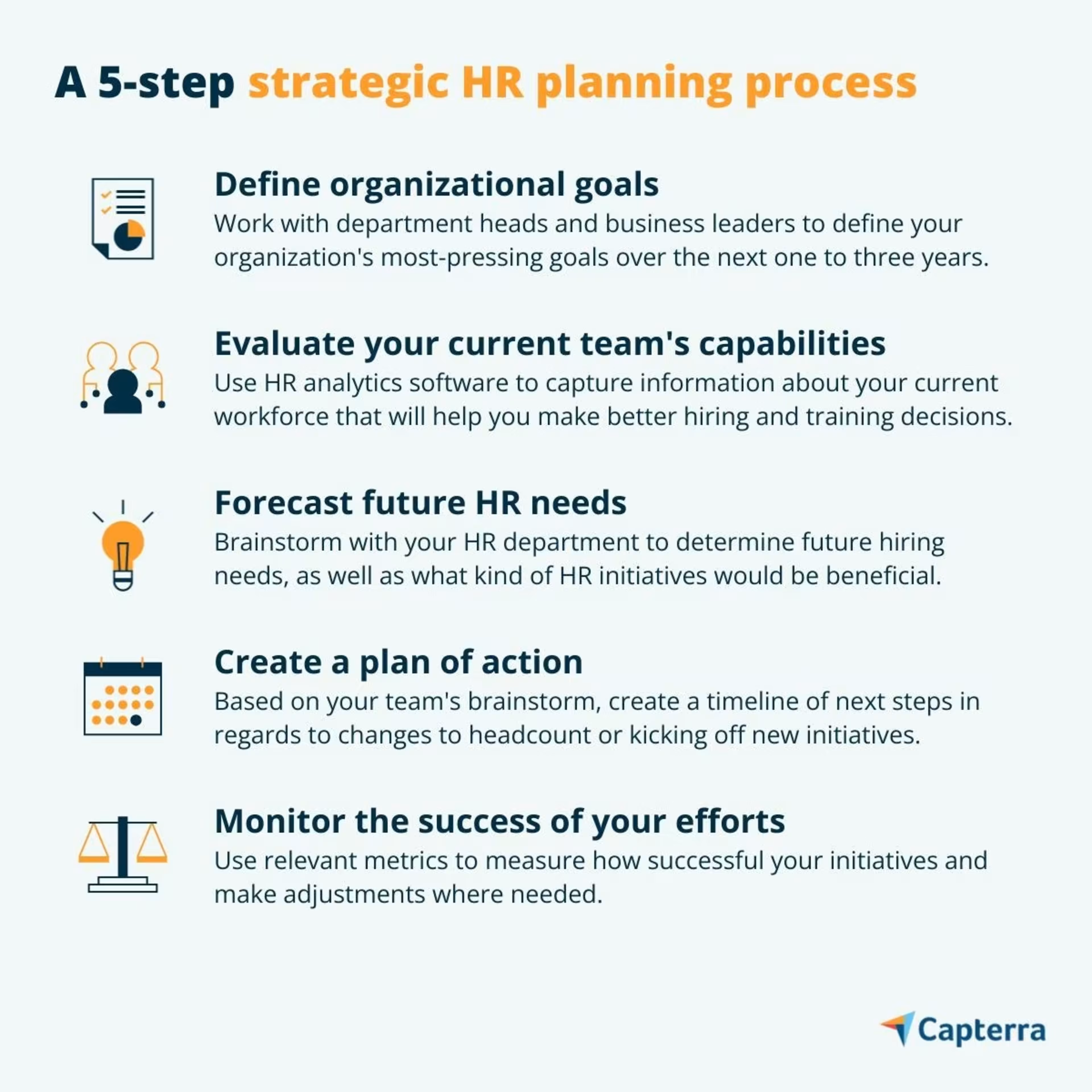
Aligning HR objectives with business goals
Strategic HR is a term that encapsulates the idea of using HR initiatives to support business goals. In practice, this looks like:
Aligning business and HR strategies
Defining HR priorities relative to critical business initiatives
Adjusting the execution of initiatives as business conditions change
In a sentence, strategic HR ensures that HR resources are allocated to projects and initiatives that will have a positive impact on the business’s bottom line. In order to accomplish this, CHROs must work with other executives to identify the most pressing business priorities and how HR can support them.
Using analytics to inform talent decisions
From compensation reports to performance metrics, every aspect of HR comes with its own comprehensive dataset that HR leaders have to understand and use to their organization’s advantage. Today, nearly every kind of HR software is built with its own workforce analytics dashboard. In many cases, these dashboards can be customized to track the metrics that are most relevant to the users who regularly access them.
Plus, there’s a whole category of tools (HR analytics platforms) that are designed to help HR practitioners make sense of their disparate workforce metrics and turn that information into action. For example, attrition data can help shed light on which business functions, teams, or roles are the most at risk for voluntary turnover, allowing HR leaders to strategically focus their retention efforts.
Forecasting, modeling, or benchmarking are all techniques that HR teams may use to make data-driven business decisions—the latter of which we’ve covered in a series of content on our blog:




Internal vs. External human resources: When and what to outsource
There are many reasons why an organization might choose to outsource some or all of its HR functions to a third party. For example, an enterprise with a large, geographically dispersed workforce may choose to outsource payroll administration so that they don’t have to keep up with tax laws in each location they operate in. Alternatively, a small, growing business with only one or two HR employees may outsource recruiting to an RPO so they can focus on core administrative duties.
Below, we’ll take a look at the pros and cons of internal and external HR, and we’ll also provide a brief overview of the main options for outsourcing talent.
Internal HR: Managing a workforce with an in-house team
Managing your organization’s HR function in-house is a challenging but rewarding undertaking. In large businesses, in-house HR teams stay efficient by building a team of professionals who each have specific roles or areas of expertise. For instance, they may have a director of employee experience, an onboarding specialist, a benefits administrator, a technical recruiter, and more. Alternatively, small businesses with in-house HR teams typically have a few HR associates who handle a broader range of responsibilities.
It may come as a surprise to learn that most businesses with an in-house HR team still outsource some processes to professional service providers. For instance, payroll outsourcing is frequently provided by payroll software vendors when an organization adopts a new system.
Internal HR: Managing a workforce with an in-house team
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
More control over HR processes: Fully managing the HR function internally gives businesses complete control over how they carry out every task, initiative, and process. | High costs: Recruiting, training, and retaining your own team of HR professionals can be cost-intensive—especially for small businesses with limited resources. |
Stronger connection to company culture and values: Having an internal team of HR professionals immersed in your organization’s culture and values enables them to align their efforts with business priorities. | Heavy administrative burden: Executing the basic tasks required to keep a business running may require your team to forego some of the strategic HR initiatives that aren’t as essential. |
Faster execution: Internal HR departments have the advantage of speed. They can quickly take action to modify policies or contact employees as needed without conferring with a third party first. | Increased risk/liability: Staying in compliance is easier for businesses when they outsource the responsibility to a third party whose job it is to stay informed and up-to-date on ever-changing legislation. |
External HR: Outsourcing aspects of talent management
Outsourcing HR can provide many advantages to businesses, from allowing them to tap into new talent pools to helping them provide competitive benefits and perks to their workforce.
A business may choose to outsource all of its HR to a full-service provider, or they may opt to have an external agency handle only specific aspects of the HR function (such as recruitment and staffing or risk management and compliance).
External HR: Outsourcing aspects of talent management
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Access to specialized and experienced providers: This is a huge benefit of outsourcing HR—you can work with providers who have years of industry-specific knowledge on their side. | Lack of control over HR processes: As we covered in the prior section, fully managing the HR function internally gives businesses complete control over every task and process. This is not the case for outsourcing, which requires ongoing back-and-forth communication to refine and adjust processes. |
Increased scalability: As a business grows, so does the strain put on the HR department that supports it. Outsourcing can help ease these growing pains by allowing businesses to quickly add or remove services as needed. | Less confidentiality: Outsourcing HR requires trusting a provider with sensitive information about employees and the business at large, which increases the risk of a data breach or leak. |
Decreased costs: Compensating, recruiting, and training an in-house HR team is expensive, which is why outsourcing HR is often the more cost-efficient option. Plus, HR service providers typically invest in the latest technology and strategies, so businesses who partner with them get the benefits of innovation without being responsible for the costs associated with it. | Potential communication and coordination issues: Partnering with a third party requires effective two-way communication, so the potential for interruptions of service or misunderstandings is high. |
INTERESTED IN HIRING A SERVICE? READ MORE

Contract and contingent workers: When to hire
There’s another kind of outsourcing relevant to HR, and that’s the outsourcing of talent. When a business hires temporary, freelance, contract, or contingent workers, this is considered outsourcing talent. Organizations may choose to outsource talent to save money, close skill gaps, or meet seasonal demands.
To learn more about the pros and cons of outsourcing with contingent workers, watch this short video:




What are some top human resources tools and software in 2023?
Most organizations have multiple tools in their HR tech stack to help them handle all of the different aspects of modern human resource management. Capterra’s HR App Sprawl Survey revealed that on average, SMBs (small to midsize businesses) use approximately five different software systems for HR purposes.**
Visit Capterra Shortlist to find the most common types of and highly rated HR tools. This research ranks 1,500+ products based on verified user reviews and ratings. Tools include:
HR software (such as HR information systems and human capital management suites)
Of course, there are many more kinds of tools available to support HR efforts, many of which are designed to perform specific tasks (such as 360 degree feedback software).
Ahead, we’ll give an overview of five categories of HR systems. But before we do, here are some considerations to keep top of mind if you’re in the process of selecting HR software for your business:
The size of your workforce: Small businesses can usually get by with one or two HR tools that offer a wide range of features, while larger businesses may have to invest in three to five different systems that each excel at supporting different tasks or processes.
Here are some of the top HR tools depending on your business size:
Which (if any) of your HR functions are handled by a service partner: If you’re not outsourcing any aspects of HR at your business, you will need to invest in more tools. If you are outsourcing, there’s a high probability that the provider you’re working with already has software to support the delivery of their services. For example, if you are outsourcing recruiting or staffing to a third party, you will likely not need to invest in an applicant tracking system or recruiting platform.
Related software systems
See a full list of HR systems that could be a fit for your business:
Your available budget: Budget significantly influences your choice of HR tools. There's a spectrum of free solutions spanning all the way to high-end ones.
An expensive tool isn't necessarily better. For the best results, compare the cost of a system against potential benefits (such as improved efficiency or faster time-to-fill). And if you’re on a tight budget, start your search with free HR tools.
Capterra has compiled several pricing reports for key HR software categories:
Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS) and Human Capital Management Suites (HCM)
Human resources information systems (HRIS) and human capital management suites (HCM) are two foundational types of HR software built with features that help businesses manage their workforce. At the core of HRIS and HCM suites are features that support administration tasks such as administering benefits, cataloging employee data, and running payroll. These systems also help automate some processes; for example, many are built with time tracking and attendance features that allow employees to manage their own schedules and request time off.
Further, many of these systems have available add-ons that support other aspects of HR. For instance, some HRIS or HCM platforms offer talent management features that streamline recruiting and onboarding efforts.
Most businesses need an HRIS or HCM platform, and some can even get by with only this type of tool in their HR tech stack if they choose a vendor that offers features beyond the basic administrative functionality.
Payroll, benefits administration, and attendance tracking tools
Payroll software, benefits administration platforms, and attendance tracking tools are all solutions that accomplish aspects of what an HRIS or HCM does.
Payroll software helps businesses accurately and efficiently manage their payroll processes in compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Typical payroll software features include tax calculation, direct deposit, and employee self-service portals. Plus, most payroll tools are easy to integrate with other HR software so that compensation information is easy to access elsewhere.
Benefits administration software is designed to help employees and HR professionals manage insurance elections, 401(k) plans, and retirement contributions in one secure location. Businesses can also use these tools to track their spending and ensure compliance with benefits eligibility regulations.
Attendance tracking tools deal with all aspects of an employee’s time. For instance, these platforms have absence management functions that allow employees to calculate their leave balances and request time off. They also typically have a calendar feature built into the platform that provides a broad view of employees’ shifts, time off, and leave.
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) and recruiting software
Recruiting teams use applicant tracking systems and/or recruiting platforms to support talent acquisition efforts. The primary difference between an ATS and a recruiting platform is that the former is focused on applicant management while the latter deals with every aspect of recruiting, from posting jobs to preparing onboarding documents. Recruiting mobile apps are also another type of tool for on-the-go recruitment.
The primary functionality of a typical ATS is candidate tracking in which recruiters can use these tools to check candidates’ progress from the first point of contact. Beyond candidate tracking, ATS can help recruiting teams parse resumes, schedule interviews, and build talent pools by organizing candidate profiles.
Recruiting software generally offers a wider range of features for sourcing, selecting, and interviewing candidates. For example, candidate management is often a functionality of recruiting platforms, but they may also have job posting, sourcing, and onboarding features.
Employee engagement software
Employee engagement software is a type of HR tool that organizations use to motivate, recognize, and reward employees. Employee engagement platforms can be purchased as stand-alone platforms or as a feature set within a more comprehensive HRIS or HCM suite, and they are considered more of a “nice-to-have” than a “need-to-have” tool.
Oftentimes, employee engagement software is built with features that help collect and analyze feedback from workers. For example, many of these tools include the ability to run employee pulse surveys. Further, they may have employee recognition capabilities such as a social media style feed where team members can publicly praise each other for their work.
Workforce management and succession planning platforms
Workforce management and succession planning platforms are tools built to support strategic HR efforts.
Workforce management software has a lot of the features you’d find in an HRIS or HCM tool that support employee operations such as employee databases, scheduling tools, and time management functionalities. However, workforce management solutions also usually have advanced analytics capabilities that help with labor forecasting and productivity management.
Succession planning software is built to assist with the process of identifying and developing employees with leadership potential. A key feature of succession planning software is competency modeling, a functionality that builds a framework of the skills, knowledge, and values needed for different key roles. Goal tracking and training management are two other features commonly found in succession planning solutions.
What are some emerging trends in human resources?
Human resources is an industry that’s constantly evolving. Innovations in technology (such as the recent explosion of ChatGPT) as well as cultural flashpoints, like the Black Lives Matter movement and the COVID-19 pandemic, have a huge impact on the way we work, necessitating ongoing adjustments within the HR industry.
Below, we’ll take a look at two trends that are shaping the future of human resources.
The importance of a diverse workforce
The bulk of today’s workforce—millennials—want to work for organizations that prioritize diversity and inclusion.[1] This preference, along with recent events such as the Black Lives Matter movement, have pushed today’s organizations to take a hard look at how they approach DEI.

It’s long been recognized that there are real business benefits to having a diverse workforce; for starters, it makes your business a more attractive place to work for underrepresented talent. But it can also improve collaboration and problem-solving when it’s done correctly because those with different ideas and perspectives within your workforce will feel empowered to speak up.




AI in HR
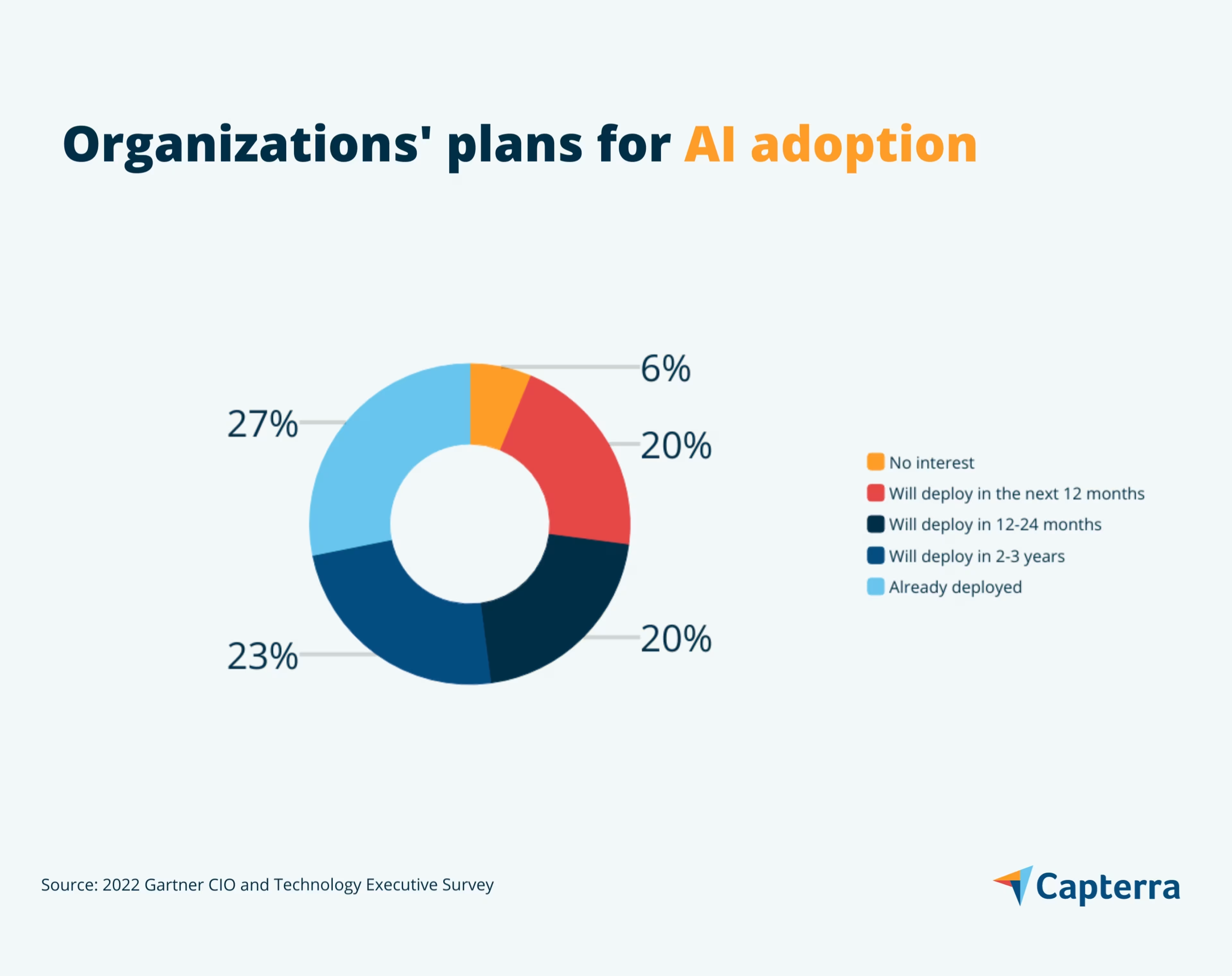
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used in software to automate different HR processes for years now, but the recent explosion of generative AI is accelerating the application of this technology. In fact, only 6% of organizations expressed no interest in deploying AI in a 2022 Gartner survey.[2]
Currently, the most common use cases for AI in HR are all centered around recruiting. For example, candidate sourcing was the most cited use case among organizations that currently use AI to automate tasks, with resume screening following closely behind.[3]
HR chatbots, which use a form of generative AI called Natural Language Understanding (NLU), are also growing in popularity. HR chatbots exist as an available feature in some HRIS and HCM systems, but they can also be standalone tools that integrate with other HR systems. HR chatbots act as assistants, providing information, answering questions, and processing common requests for employees and job seekers alike.
Read more on the topic of AI in HR



Download Capterra’s free skills gap analysis template
As an HR professional, you know how important it is to identify and acquire the skills your organization needs to be successful now and in the future. Conducting a skills gap analysis—a process in which HR leaders identify missing skills in their workforce and develop a plan to fill them—is an effective strategy you can use to accomplish this.
Below, download our free skills gap analysis template, a tool you can use to catalog the skills needed in a specific team or department and compare them to the ones current team members already have.

